| [1] Blanié A,Bellamy L,Rhayem Y,et al.Duration of Postoperative Fibrinolysis after Total Hip or Knee Replacement: A Laboratory Follow-up Study.Thromb Res.2013;131(1):e6-e11.
[2] Li B,Wen Y,Wu H,et al.The effect of tourniquet use on hidden blood loss in total knee arthroplasty.Int Orthop. 2009;33(5):1263-1268.
[3] Lopez-Balderas N,Bravo E,Camara M,et al.Seroprevalence of hepatitis viruses and risk factors in blood donors of Veracruz,Mexico.J Infect Dev Ctries. 2015;9(3):274-282.
[4] Sehat KR,Evans R,Newman JH.How much blood is really lost in total knee arthroplasty?. Correct blood loss management should take hidden loss into account. Knee.2000;7(3):151-155.
[5] Levine BR,Haughom B,Strong B,et al.Blood Management Strategies for Total Knee Arthroplasty.J Am Acad Orthop Surg.2014;22(6):361-371.
[6] Oberhofer D,Sakic K,Jankovic S,et al.How to improve perioperative blood management in patients undergoing total hip or knee replacement surgery? Lijec Vjesn.2012;134(11-12):322-327.
[7] Shemshaki H,Nourian SM,Nourian N,et al.One step closer to sparing total blood loss and transfusion rate in total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis of different methods of tranexamic acid administration.Arch Orthop Trauma Surg.2015;135(4):573-588.
[8] Wu Q,Zhang HA,Liu SL,et al.Is tranexamic acid clinically effective and safe to prevent blood loss in total knee arthroplasty? A meta-analysis of 34 randomized controlled trials. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol.2015;25(3):525-541.
[9] Sorin A,Claeys M,D'Haese J,et al.Reduction of blood loss by tranexamic acid in total knee replacement.J Bone Joint Surg Br.1999;(Suppl.II):518-520.
[10] Erstad BL. Systemic hemostatic medications for reducing surgical blood loss.Ann Pharmacother. 2001; 35(7-8):925-934.
[11] Dunn CJ,Goa KL.Tranexamic acid-A review of its use in surgery and other indications.Drugs.1999;57(6): 1005-1032.
[12] Lin C,Shuhaiber JH,Loyola H,et al.The Safety and Efficacy of Antifibrinolytic Therapy in Neonatal Cardiac Surgery. PLoS One.2015;10(5):e126514.
[13] Verstraete M.Clinical application of inhibitors of fibrinolysis.Drugs.1985;29(3):236-261.
[14] Suenson E,Lutzen O,Thorsen S.Initial plasmin-degradation of fibrin as the basis of a positive feed-back mechanism in fibrinolysis.Eur J Biochem. 1984;140(3):513-522.
[15] Fergusson DA,Hebert PC,Mazer CD,et al.A comparison of aprotinin and lysine analogues in high-risk cardiac surgery.N Engl J Med.2008;358(22): 2319-2331.
[16] Henry D,Carless P,Fergusson D,et al.The safety of aprotinin and lysine-derived antifibrinolytic drugs in cardiac surgery: a meta-analysis.Can Med Assoc J. 2009;180(2):183-193.
[17] Shakur H,Roberts I,Bautista R,et al.Effects of tranexamic acid on death, vascular occlusive events, and blood transfusion in trauma patients with significant haemorrhage (CRASH-2): a randomised, placebo-controlled trial.Lancet.2010;376(9734):23-32.
[18] Meybohm P,Herrmann E,Nierhoff J,et al.Aprotinin May Increase Mortality in Low and Intermediate Risk but Not in High Risk Cardiac Surgical Patients Compared to Tranexamic Acid and ε-Aminocaproic Acid-A Meta-Analysis of Randomised and Observational Trials of over 30 000 Patients.PloS One.2013;8(3):e58009.
[19] McCormack PL.Tranexamic Acid: A Review of its Use in the Treatment of Hyperfibrinolysis. Drugs.2012; 72(5): 585-617.
[20] Benoni G,Carlsson A,Petersson C,et al.Does tranexamic acid reduce blood loss in knee arthroplasty? Am J Knee Surg.1995;8(3):88-92.
[21] Wong J,Abrishami A,El Beheiry H,et al.Topical Application of Tranexamic Acid Reduces Postoperative Blood Loss in Total Knee Arthroplasty A Randomized, Controlled Trial.J Bone Joint Surg Am.2010;92A(15): 2503-2513.
[22] Wang C,Xu G,Han Z,et al.Topical application of tranexamic acid in primary total hip arthroplasty: A systemic review and meta-analysis.Int J Surg.2015; 15:134-139.
[23] Alshryda S,Sukeik M,Sarda P,et al.A systematic review and meta-analysis of the topical administration of tranexamic acid in total hip and knee replacement. Bone Joint J.2014;96-B(8):1005-1015.
[24] Ishida K,Tsumura N,Kitagawa A,et al.Intra-articular injection of tranexamic acid reduces not only blood loss but also knee joint swelling after total knee arthroplasty.Int Orthop.2011;35(11):1639-1645.
[25] Iwai T,Tsuji S,Tomita T,et al.Repeat-dose intravenous tranexamic acid further decreases blood loss in total knee arthroplasty.Int Orthop.2013;37(3):441-445.
[26] Moher D,Cook DJ,Eastwood S,et al.Improving the quality of reports of meta-analyses of randomized controlled trials: the QUOROM Statement.Rev Esp Salud Publica.2000;74(2):107-118.
[27] Moher D,Liberati A,Tetzlaff J,et al.Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement.Int J Surg.2010;8(5):336-341.
[28] Maniar RN,Kumar G,Singhi T,et al.Most effective regimen of tranexamic acid in knee arthroplasty: a prospective randomized controlled study in 240 patients.Clin Orthop Relat Res.2012;470(9):2605- 2612.
[29] Higgins JPT,Thompson SG.Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta-analysis.Stat Med. 2002;21(11):1539-1558.
[30] Seo JG,Moon YW,Park SH,et al. The comparative efficacies of intra-articular and IV tranexamic acid for reducing blood loss during total knee arthroplasty.Knee Surg.Sports Traumatol Arthrosc.2013;21(8): 1869-1874.
[31] Soni A,Saini R,Gulati A,et al.Comparison between intravenous and intra-articular regimens of tranexamic acid in reducing blood loss during total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty.2014;29(8):1525-1527.
[32] Patel JN,Spanyer JM,Smith LS,et al.Comparison of intravenous versus topical tranexamic acid in total knee arthroplasty: a prospective randomized study.J Arthroplasty.2014;29(8):1528-1531.
[33] Sarzaeem MM,Razi M,Kazemian G,et al.Comparing efficacy of three methods of tranexamic acid administration in reducing hemoglobin drop following total knee arthroplasty.J Arthroplasty.2014;29(8): 1521-1524.
[34] Gomez-Barrena E,Ortega-Andreu M,Padilla-Eguiluz NG,et al.Topical Intra-Articular Compared with Intravenous Tranexamic Acid to Reduce Blood Loss in Primary Total Knee Replacement: A Double-Blind, Randomized, Controlled, Noninferiority Clinical Trial.J Bone J Surg.2014;96(23):1937-1944.
[35] Benoni G,Lethagen S,Fredin H.The effect of tranexamic acid on local and plasma fibrinolysis during total knee arthroplasty.Thromb Res.1997;85(3): 195-206.
[36] Jansen AJ,Andreica S,Claeys M,et al.Use of tranexamic acid for an effective blood conservation strategy after total knee arthroplasty.Br J Anaesth. 1999;83(4):596-601.
[37] Panteli M,Papakostidis C,Dahabreh Z,et al.Topical tranexamic acid in total knee replacement: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Knee.2013;20(5):300-309.
[38] Alshryda S,Sarda P,Sukeik M,et al.Tranexamic acid in total knee replacement: a systematic review and meta-analysis.J Bone Joint Surg Br.2011;93(12):1577- 1585.
[39] Wang H,Shen B,Zeng Y.Comparison of topical versus intravenous tranexamic acid in primary total knee arthroplasty: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled and prospective cohort trials.Knee.2014;21(6):987- 993.
[40] Shemshaki H,Nourian SMA,Nourian N,et al.One step closer to sparing total blood loss and transfusion rate in total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis of different methods of tranexamic acid administration.Arch Orthop Trauma Surg.2015;135(4):573-588. |
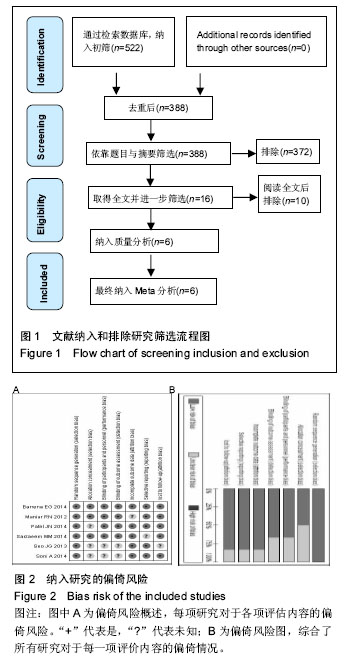
.jpg)

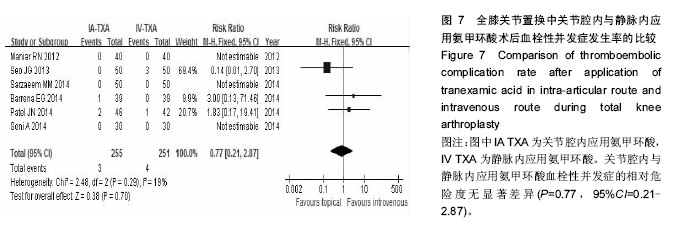
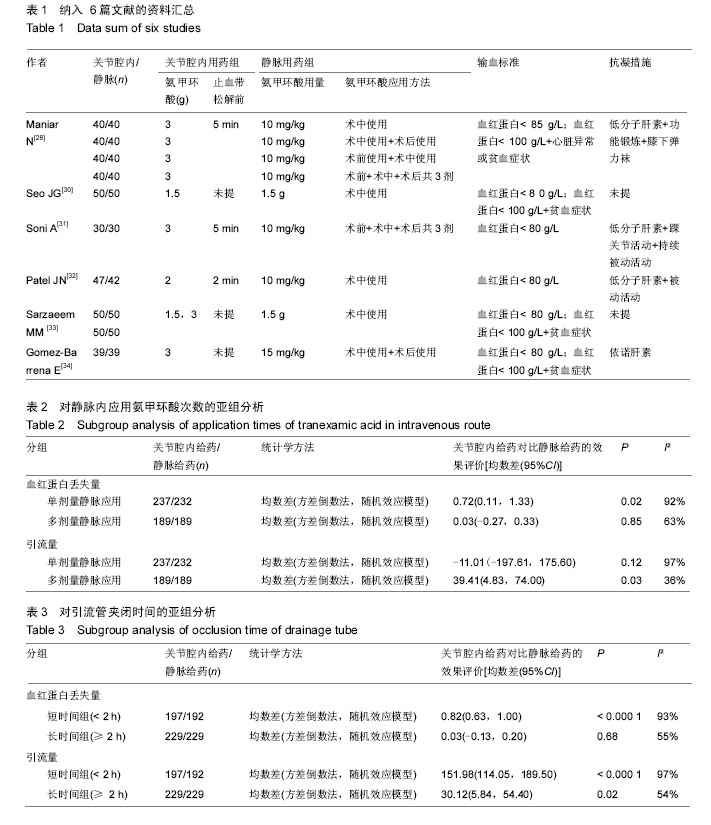
.jpg)